
Cervical Spondylosis(Arthritis of the Neck)
Cervical spondylosis is a disorder in which there is abnormal wear on the cartilage and bones of the neck (cervical vertebrae). It is a common cause of chronic neck pain. Cervical spondylosis is the degeneration of the joints in the neck.
Cause -
1. Loss of Water –
In children and young adults, disks have high water content. As we get older, our disks begin to dry out and weaken. This problem causes settling, or collapse, of the disk spaces and loss of disk space height.
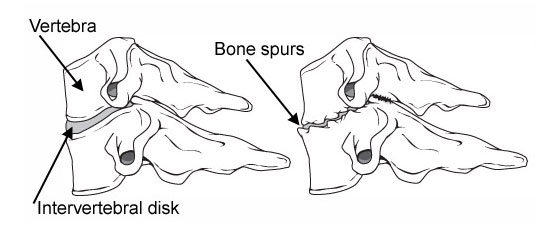
2. Disk Degeneration and Bone Spurs –
As the facet joints experience increased pressure, they also begin to degenerate and develop arthritis, similar to the hip or knee joint. The cartilage that covers and protects the joints wears away.
If the cartilage wears away completely, it can result in bone rubbing on bone. To make up for the lost cartilage, your body may respond by growing new bone in your facet joints to help support the vertebrae. Over time, this bone overgrowth (spurs) may narrow the space for the nerves to pass through (stenosis).
3. Built of the body - Persons having thick neck with a Dowager's Hump and long backs are much prone to spondylosis.
4. Occupational stresses-
a) Officers, typists and others working on poorly and wrongly positioned desks and tables.
b) Drivers prone to prolonged driving.
c) Persons involved in occupations including lifting and carrying things on their head.
d) Habit of holding phone on one shoulder while talking.
e) Sleeping in awkward positions, using inappropriate pillows.
Site -
The segments commonly affected in the cervical region are C4 to T1
Risk Factors -
There are several factors that increase your risk for cervical spondylosis.
1. Genetics - if your family has a history of neck pain
2. Smoking - clearly linked to increased neck pain
3. Occupation - jobs with lots of neck motion and overhead work
4. Mental health issues - depression/anxiety
5. Injuries/trauma - car wreck or on-the-job injury
Symptoms -
1. Neck stiffness and pain
2. Headache
3. Pain in the shoulder or arms
4. Inability to fully turn the head or bend the neck, sometimes interfering with driving
5. Grinding noise or sensation when the neck is turned
6. Symptoms are most severe in the morning and again at the end of the day.
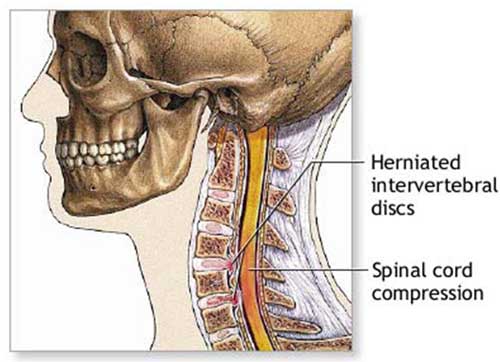
7. Cervical spondylosis with myelopathy - If cervical spondylosis results in pressure on the spinal cord (cervical stenosis), a condition called cervical myelopathy.
• Tingling, numbness, and weakness in the arms, hands, legs, or feet
• Lack of coordination and difficulty walking
• Abnormal reflexes
• Muscle spasms
• Loss of control over bladder and bowel
• When bone spurs press on nerves .Pain shooting down into one or both arms.
8. Postural disturbance:
• Stress at C5, C6 so tightness of upper cervical spine extensors.
• Chin placed forward.
• Kyphosis of thoracic spine.
• Tight pectorals.
• Flattened, sometimes lordotic lumbar spine.
• Flexion of elbows and hand.
9. vertigo
Investigation -
1. X-rays
2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
3. Computed tomography (CT) scans
4. Myelography
5. Electromyography (EMG)
Aims of Physiotherapy Treatment -
1. To relieve pain
2. To provide support to the neck
3. To restore the neck movements in full range
4. To re-educate the patient for posture correction
5. To strengthen the cervical muscles
6. To analyses the basic precipitating causes of the patient's problem and aim at alleviating those causative factors
Physiotherapy Treatment -
1. Heat Modalities
2. Neck Exercises
3. Manipulative Therapy
4. Hydrotherapy
5. Postural Awareness
6. Relaxation
7. Cervical traction
8. Neck support

