
Meniscus Ligament Tear
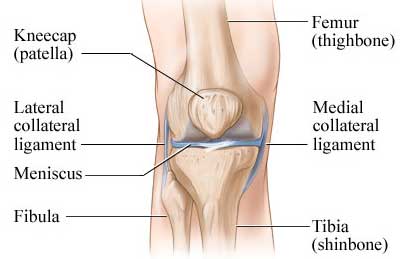 A meniscus tear is a common knee injury. The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc that cushions your knee.
A meniscus tear is a common knee injury. The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc that cushions your knee.
Each knee has two menisci (plural of meniscus)-one at the outer edge of the knee and one at the inner edge.
The menisci keep your knee steady by balancing your weight across the knee. A torn meniscus can prevent your knee from working right.
Cause -
1. When the leg is twisting or turning quickly, with the foot planted and knee is bent.
2. when we lift something heavy or play sports.
3. In old age, meniscus gets worn. This can make it tear more easily.
Symptoms -
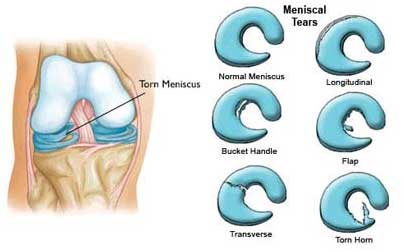
• Minor Tear- slight pain and swelling and goes away in 3 weeks.
• You might feel a "pop" when you tear a meniscus.
• Pain
• Stiffness and swelling
• Catching or locking of your knee
• The sensation of your knee "giving way"
• You are not able to move your knee through its full range of motion
Investigation -
x-ray and MRI
Treatment-
• The outside one-third of the meniscus has a rich blood supply. A tear in this "red" zone may heal on its own, or can often be repaired with surgery. A longitudinal tear is an example of this kind of tear.
• The inner two-thirds of the meniscus lacks a blood supply. Without nutrients from blood, tears in this "white" zone cannot heal. These complex tears are often in thin, worn cartilage. Because the pieces cannot grow back together, tears in this zone are usually surgically trimmed away.
• Along with the type of tear you have, your age, activity level, and any related injuries will factor into your treatment plan.
• RICE: The RICE protocol is effective for most sports-related injuries. RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
• Rest: Take a break from the activity that caused the injury. Use crutches to avoid putting weight on your leg.
• Ice: Use cold packs for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
• Compression: To prevent additional swelling and blood loss, wear an elastic compression bandage.
• Elevation: To reduce swelling, recline when you rest, and put your leg up higher than your heart.
Physiotherapy-
• Exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstring muscles of the upper leg.
• Modalities for pain relief.
• Postural guidance.

