
Spinal Stenosis
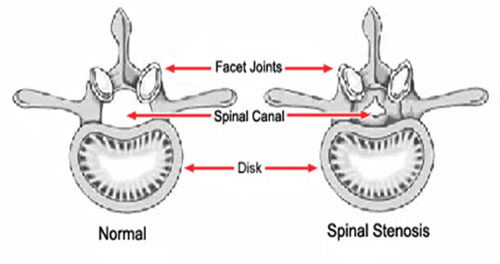 Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that may occur in any of the regions of the spine. This narrowing causes a restriction to the spinal canal, resulting in a neurological deficit
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that may occur in any of the regions of the spine. This narrowing causes a restriction to the spinal canal, resulting in a neurological deficit
Cause -
1. Aging
All the factors below may cause the spaces in the spine to narrow,
Bodys ligaments can thicken (ligamentum flavum)
Bone spurs develop on the bone and into the spinal canal
Intervertebral discs may bulge or herniate into the canal
Facet joints break down
Compression fractures of the spine, which are common in osteoporosis
Cysts form on the facet joints causing compression of the spinal sack of nerves (thecal sac)
2. Arthritis
Two types
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
3. Heredity
Spinal canal is too small at birth
Structural deformities of the vertebrae may cause narrowing of the spinal canal
4. Instability of the spine or spondylolisthesis
5. Trauma
Accidents and injuries may dislocate the spine and the spinal canal or cause burst fractures that yield fragments of bone that go through the canal
6. Tumors of the spine
Irregular growths of soft tissue will cause inflammation
Growth of tissue into the canal pressing on nerves, the sac of nerves, or the spinal cord.
Symptom -
1. Common
Standing discomfort (94%)
Numbness (63%)
Weakness (43%)
Bilateral symptoms (68%)
Discomfort above and below knee (78%)
Buttock / Thigh only (15%)
Below the knee (7%)
2. Neurological disorders
Pinched nerve
Intermittent neurogenic claudication
Weakness
Diffuse or radicular leg pain
Paresthesis (bilaterally)
Weakness heaviness in buttocks radiating into lower extremities with walking or prolonged standing.
Symptoms occur with extension of spine and are relieved with spine flexion.
Minimal to zero symptoms when seated or supine.
3. Other
Fever
Nocturnal pain
Gait disturbance
Structural deformity
Unexplained weight loss
Previous carcinoma
Severe pain upon lying down
progressive neurologic deficit
degenerative disc or joint changes
Narrowing of spinal canal, nerve root canal or intervertebral Canal Stenosis
Diagnostic procedures -
X-ray
CT scan
MRI
EMG (Electromyography)
NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity)
Physiotherapy Treatment-
Ultrasonic diathermy
Shortwave diathermy
Heat/cold therapy
TENS
Low level laser therapy
Intermittent traction
Therapeutic exercise

